Solution of SEAMO 2017 Paper D - Southeast Asian Mathematical Olympiads

SEAMO 2017 PAPER D
SEAMO 2017 Paper D No. 1
Find the value of $x$ in $\frac{x}{3+x}-\frac{x}{4-x}=2$.A. $-12$
B. +12
C. $-24$
D. +24
E. +30
Solution: Show/Hide
$\begin{align}\frac{x}{3+x}-\frac{x}{4-x} &= 2 \\ \frac{x(4-x)-x(3+x)}{(3+x)(4-x)} &= 2 \\ \frac{4x-x^2-3x-x^2}{12-3x+4x-x^2} &= 2 \\ \frac{x-2x^2}{12+x-x^2} &= 2 \\ 24+2x-2x^2 &= x-2x^2 \\ x &= -24 \end{align}$Answer: C
SEAMO 2017 Paper D No. 2
Find all positive value of $n$, such that ${{2}^{n}}-1$ is divisible by 7.A. $n$ must be a multiple of 2
B. $n$ must be a multiple of 3
C. $n$ must be a multiple of 4
D. $n$ must be a multiple of 5
E. None of the above
Solution: Show/Hide
Consider $2^3=8\equiv 1(\bmod 7)$The congruency holds for $k$ power.
$2^{3k}\equiv 1(\bmod 7)$
Thus, $n=3k$
Which is a multiple of 3.
Answer: B
SEAMO 2017 Paper D No. 3
Type A and B coffee are mixed in the ratio $m:n$ and costs $40 and $60 per kg, respectively. If the price of type A coffee is decreased by 15% while the price of type B coffee is increased by 15%, the total cost of the mixture remained unchanged. Find $m:n$.A. 1 : 2
B. 2 : 3
C. 3 : 2
D. 2 : 1
E. 5 : 2
Solution: Show/Hide
$\begin{align}40m+60n &= 0.85\times 40m+1.15\times 60n \\ 40m+60n &= 34m+69n \\ 6m &= 9n \\ \frac{m}{n} &= \frac{9}{6} \\ \frac{m}{n} &= \frac{3}{2} \end{align}$Answer: C
SEAMO 2017 Paper D No. 4
Evaluate $\frac{400^2\times (254^2+246^2)\times (254^4+246^4)}{(254^8-246^8)}$A. 30
B. 40
C. 50
D. 60
E. 70
Solution: Show/Hide
$\frac{400^2\times (254^2+246^2)\times (254^4+246^4)}{(254^8-246^8)}$= $\frac{400^2\times (254^2+246^2)\times (254^4+246^4)}{(254^4-246^4)(254^4+246^4)}$
= $\frac{400^2\times (254^2+246^2)}{(254^4-246^4)}$
= $\frac{400^2\times (254^2+246^2)}{(254^2-246^2)(254^2+246^2)}$
= $\frac{400^2}{254^2-246^2}$
= $\frac{{{400}^{2}}}{(254-246)(254+246)}$
= $\frac{400\times 400}{8\times 500}$
= 40
Answer: B
SEAMO 2017 Paper D No. 5
Evaluate $\frac{20172016^2}{20172015^2+20172017^2-2}$.A. $\frac{1}{3}$
B. $\frac{1}{2}$
C. 1
D. $\frac{3}{2}$
E. None of the above
Solution: Show/Hide
$\frac{20172016^2}{20172015^2+20172017^2-2}$Let $x=20172016$
$\frac{x^2}{{{(x-1)}^{2}}+{{(x+1)}^{2}}-2}$
= $\frac{x^2}{x^2-2x+1+x^2+2x+1-2}$
= $\frac{x^2}{2x^2}$
= $\frac{1}{2}$
Answer: B
SEAMO 2017 Paper D No. 6
It is known that $m=\frac{a}{b+c}=\frac{b}{a+c}=\frac{c}{a+b}$. Given that $a+b+c\ne 0$, find the value of $m$.A. $\frac{1}{4}$
B. $\frac{1}{3}$
C. $\frac{1}{2}$
D. 1
E. None of the above
Solution: Show/Hide
Method 1:We observe when $\frac{a_1}{b_1}=\frac{a_2}{b_2}=...=\frac{a_n}{b_n}$ given $a_1+a_2+...+a_n\ne 0$, then $\frac{a_1}{b_1}=\frac{a_2}{b_2}=...=\frac{a_n}{b_n}$ = $\frac{a_1+a_2+...+a_n}{b_1+b_2+...+b_n}$.
$\begin{align}m &= \frac{a+b+c}{b+c+a+c+a+b} \\ &= \frac{(a+b+c)}{2(a+b+c)} \\ m &= \frac{1}{2} \end{align}$
Method 2:
Let $a=b=c$
$\begin{align}m &= \frac{a}{b+c} \\ &= \frac{a}{a+a} \\ &= \frac{a}{2a} \\ m &= \frac{1}{2} \end{align}$
Answer: C
SEAMO 2017 Paper D No. 7
A rectangle is inscribed in a square as shown. It is known that the total area of 4 isosceles right angled $\Delta $ is 98 $\text{cm}^2$. Find $\text{XY}$, the length of the diagonal of rectangle.
A. 10
B. 11
C. 12
D. 13
E. 14
Solution: Show/Hide

Area of
$\begin{align}\Delta s &= 98 \\ \frac{1}{2}\times m^2\times 2+\frac{1}{2}\times n^2\times 2 &= 98 \\ m^2+n^2 &= 98 \end{align}$
$\begin{align}(\text{XY})^2 &= (m+n)^2+(m-n)^2 \\ &= m^2+2mn+n^2+m^2-2mn+n^2 \\ &= 2(m^2+n^2) \\ &= 2\times 98 \\ (\text{XY})^2 &= 196 \\ \text{XY} &= 14 \end{align}$
Answer: E
SEAMO 2017 Paper D No. 8
Evaluate $\left( \frac{2}{3}+\frac{3}{4}+...+\frac{49}{50} \right)$$\left( \frac{1}{2}+\frac{2}{3}+\frac{3}{4}...+\frac{48}{49} \right)$-$\left( \frac{1}{2}+\frac{2}{3}+\frac{3}{4}...+\frac{49}{50} \right)$$\left( \frac{2}{3}+\frac{3}{4}+...+\frac{48}{49} \right)$.A. $\frac{49}{100}$
B. $\frac{99}{100}$
C. $\frac{49}{50}$
D. $\frac{48}{50}$
E. 1
Solution: Show/Hide
$\left( \frac{2}{3}+\frac{3}{4}+...+\frac{49}{50} \right)$$\left( \frac{1}{2}+\frac{2}{3}+\frac{3}{4}...+\frac{48}{49} \right)$-$\left( \frac{1}{2}+\frac{2}{3}+\frac{3}{4}...+\frac{49}{50} \right)$$\left( \frac{2}{3}+\frac{3}{4}+...+\frac{48}{49} \right)$Let $x=\frac{2}{3}+\frac{3}{4}+...+\frac{48}{49}$
$\left( \frac{2}{3}+\frac{3}{4}+...+\frac{48}{49}+\frac{49}{50} \right)$$\left( \frac{1}{2}+\frac{2}{3}+\frac{3}{4}...+\frac{48}{49} \right)$-$\left( \frac{1}{2}+\frac{2}{3}+\frac{3}{4}...+\frac{48}{49}+\frac{49}{50} \right)$$\left( \frac{2}{3}+\frac{3}{4}+...+\frac{48}{49} \right)$
= $\left( x+\frac{49}{50} \right)\left( \frac{1}{2}+x \right)$-$\left( \frac{1}{2}+x+\frac{49}{50} \right)x$
= $\frac{1}{2}x+x^2$+$\frac{49}{100}$+$\frac{49}{50}x$-$\frac{1}{2}x$-$x^2$-$\frac{49}{50}x$
= $\frac{49}{100}$
Answer: A
SEAMO 2017 Paper D No. 9
Evaluate $\sqrt{2017+2016\sqrt{2017+2016\sqrt{2017+2016\sqrt{...}}}}$A. 2015
B. 2016
C. 2017
D. 2018
E. 2019
Solution: Show/Hide
Let $x=\sqrt{2017+2016\sqrt{2017+2016\sqrt{2017+2016\sqrt{...}}}}$Then,
$x=\sqrt{2017+2016x}$
$x^2=2017+2016x$
$x^2-2016x-2017=0$
$(x-2017)(x+1)=0$
$x=2017$
Answer: C
SEAMO 2017 Paper D No. 10
It is given that $a+\frac{1}{a}=5$, find $a^4+\frac{1}{a^4}$.A. 523
B. 527
C. 631
D. 635
E. None of the above
Solution: Show/Hide
$a+\frac{1}{a}=5$$\begin{align}\left( a+\frac{1}{a} \right)^2 &= 5^2 \\ a^2+2.a.\frac{1}{a}+\frac{1}{a^2} &= 25 \\ a^2+\frac{1}{a^2}+2 &= 25 \\ a^2+\frac{1}{a^2} &= 23 \end{align}$
$\begin{align}\left( a^2+\frac{1}{a^2} \right)^2 &= 23^2 \\ a^4+2.a^2.\frac{1}{a^2}+\frac{1}{a^4} &= 529 \\ a^4+\frac{1}{a^4}+2 &= 529 \\ a^4+\frac{1}{a^4} &= 527 \end{align}$
Answer: B
SEAMO 2017 Paper D No. 11
Evaluate ${{\log }_{\frac{1}{2}}}8+{{\log }_{2}}64-{{\log }_{5}}\frac{1}{125}$.A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
E. 6
Solution: Show/Hide
${{\log }_{\frac{1}{2}}}8+{{\log }_{2}}64-{{\log }_{5}}\frac{1}{125}$= ${{\log }_{\frac{1}{2}}}{{\left( \frac{1}{2} \right)}^{-3}}+{{\log }_{2}}{{2}^{6}}-{{\log }_{5}}{{5}^{-3}}$
= $-3+6-(-3)$
= 6
Answer: E
SEAMO 2017 Paper D No. 12
ABCD is a rectangle with E the midpoint of AB and $DF\bot CE$. Given that AB = 6 and BC = 4. Find length of DF.
A. 3.6
B. 4.2
C. 4.8
D. 5.4
E. None of the above
Solution: Show/Hide

$\begin{align}CE &= \sqrt{BE^2+CB^2} \\ &= \sqrt{\left( \frac{AB}{2} \right)^2+CB^2} \\ &= \sqrt{3^2+4^2} \\ CE &= 5 \end{align}$
Area of rectangle ABCD = AD.CD
Area of $\Delta CDE$ = $\frac{1}{2}.AD.CD$
Area of rectangle ABCD = 2.$\Delta CDE$.
$\begin{align}AB.BC &= 2.\frac{1}{2}.DF.CE \\ 6\times 4 &= DF\times 5 \\ DF &= \frac{24}{5} \\ DF &= 4.8 \end{align}$
Answer: C
SEAMO 2017 Paper D No. 13
The smallest number which, when divided by 52 leaves a remainder 33, when divided by 78 leaves 59 as remainder and when divided by 117 leaves 98 as remainder isA. 553
B. 293
C. 468
D. 449
E. 458
Solution: Show/Hide
52 – 33 = 1978 – 59 = 19
117 – 98 = 19
It suffices to find the lowest common multiple of 52, 78, 117.

LCM is $13\times 3\times 2\times 2\times 1\times 3=468$.
468 – 19 = 449
Answer: D
SEAMO 2017 Paper D No. 14
In the figure shown below, the area of $\Delta ABC$ is 8 $\text{cm}^2$, AE = DE and BD = 2CD. Find the total area of the shaded regions.
A. 3.2 $\text{cm}^2$
B. 3.6 $\text{cm}^2$
C. 4.0 $\text{cm}^2$
D. 4.4 $\text{cm}^2$
E. None of the above
Solution: Show/Hide
$\frac{[BDF]}{[CDF]}=\frac{BD}{CD}=\frac{2}{1}$$[CDF]=\frac{x+y}{2}$
[ABE] + [EBD] + [AEF] + [DEF] + [DFC] = [ABC]
$\begin{align}x+x+y+y+\frac{x+y}{2} &= 8 \\ 2x+2y+\frac{x+y}{2} &= 8 \\ 2(x+y)+\frac{1}{2}(x+y) &= 8 \\ \frac{5}{2}(x+y) &= 8 \\ x+y &= 8\times \frac{2}{5} \\ x+y &= 3.2\,\text{cm}^2 \end{align}$
Answer: A
SEAMO 2017 Paper D No. 15
In $\Delta ABC$, AN = BM = AB, $\angle C=38^\circ$. Find $\angle APB$.
A. $114^\circ$
B. $104^\circ$
C. $118^\circ$
D. $120^\circ$
E. $122^\circ$
Solution: Show/Hide
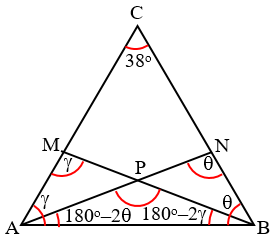
$\gamma +\theta =142^\circ$
$\begin{align}\angle APB &= 180^\circ -[360^\circ -2(\theta +\gamma)] \\ &= 180^\circ -[360^\circ -2\times 142^\circ] \\ &= 180^\circ -[360^\circ -284^\circ] \\ &= 180^\circ -76^\circ \\ &= 104^\circ \end{align}$
Answer: B
SEAMO 2017 Paper D No. 16
$p$ is the difference between a real number and its reciprocal. $q$ is the difference between the square of the same real number and the square of the reciprocal. The the value of $p^4+q^2+4p^2$ isA. $2q^2$
B. $3q^2$
C. $\frac{1}{2}q^2$
D. $\frac{3}{4}q^2$
E. None of the above
Solution: Show/Hide
$q=x^2-\frac{1}{x^2}$$\begin{align}p &= x-\frac{1}{x} \\ p^2 &= \left( x-\frac{1}{x} \right)^2 \\ p^2 &= x^2-2+\frac{1}{x^2} \end{align}$
$\begin{align}p^4+4p^2 &= (p^2+2)^2-4 \\ &= \left( x^2-2+\frac{1}{x^2}+2 \right)^2-4 \\ &= \left( x^2+\frac{1}{x^2} \right)^2-4 \\ &= x^4+2+\frac{1}{x^4}-4 \\ &= \left( x^4-2+\frac{1}{x^4} \right) \\ &= \left( x^2-\frac{1}{x^2} \right)^2 \\ p^4+4p^2 &= q^2 \end{align}$
$\begin{align}p^4+q^2+4p^2 &= p^4+4p^2+q^2 \\ &= q^2+q^2 \\ &= 2q^2 \end{align}$
Answer: A
SEAMO 2017 Paper D No. 17
A motorboat takes 6 h to travel from port A to port B, which is on the same side of the river. It takes the boat 8 h, to return to port A. It is given the speed of the current is 2.5 km/h. Find the speed of the boat in still water.A. 10.5 km/h
B. 13.5 km/h
C. 16.5 km/h
D. 17.5 km/h
E. 18.5 km/h
Solution: Show/Hide
Time from port A to B: $t_1$ = 6 hTime from port B to A: $t_2$ = 8 h
Speed of the current: $v_{current}$ = 2.5 h
Let:
$v_{boat}$ be the speed of the boat in still water (in km/h).
$d$ be distance between A and B (in km).
The boat’s relative speed:
Downstream (with the current):
$v_{down}=v_{boat}+v_{current}$
Upstream (against the current):
$v_{up}=v_{boat}-v_{current}$
Using the relationship:
distance = speed $\times $ time:
Downstream:
$\begin{align}d &= v_{down}.t_1 \\ &= t_1.\left( v_{boat}+v_{current} \right) \\ &= 6\left( v_{boat}+2.5 \right) \\ d &= 6v_{boat}+15\,....\,(1) \end{align}$
Upstream:
$\begin{align}d &= v_{up}.t_2 \\ &= t_2.\left( v_{boat}-v_{current} \right) \\ &= 8\left( v_{boat}-2.5 \right) \\ d &= 8v_{boat}-20\,....\,(2) \end{align}$
From equation (1) and (2):
$\begin{align}8v_{boat}-20 &= 6v_{boat}+15 \\ 2v_{boat} &= 35 \\ v_{boat} &= 17.5 \end{align}$
Answer: D
SEAMO 2017 Paper D No. 18
Given an equilateral triangle, what is the ratio of area of its inscribed circle to the area of its circumscribed circle?
A. 1 : 2
B. 1 : 3
C. 1 : 4
D. 1 : 5
E. None of the above
Solution: Show/Hide

$R=2r$
Area of its inscribed circle = $\pi r^2$
Area of its circumscribed circle = $\pi r^2$ = $\pi (2r)^2$ = $\pi .4r^2$
Ratio of tis inscribed circle to the area of its circumscribed circle is:
$\pi r^2:\pi .4r^2$ = 1 : 4
Answer: C
SEAMO 2017 Paper D No. 19
Arrange $3^{50}$, $4^{40}$, $5^{30}$ in ascending order.A. $3^{50} < 4^{40} < 5^{30}$
B. $5^{30} < 3^{50} < 4^{40}$
C. $5^{30} < 4^{40} < 3^{50}$
D. $4^{40} < 5^{30} < 3^{50}$
E. None of the above
Solution: Show/Hide
$3^{50}=3^{5\times 10}=(3^5)^{10}=243^{10}$$4^{40}=4^{4\times 10}=(4^4)^{10}=256^{10}$
$5^{30}=5^{3\times 10}=(5^3)^{10}=125^{10}$
$125^{10} < 243^{10} < 256^{10}$
$5^{30} < 3^{50} < 4^{40}$
Answer: B
SEAMO 2017 Paper D No. 20
Sara picks 2 oranges from a basket of 15 oranges in which 10 oranges are good, 5 oranges are bad. The probability that she picks up at least one good orange is $\frac{m}{n}$. Find the value of $(m+n)$.A. 38
B. 39
C. 40
D. 41
E. 42
Solution: Show/Hide
$\begin{align}\frac{m}{n} &= \frac{C_1^{10}\times C_1^5+C_2^{10}}{C_2^5} \\ &= \frac{\frac{10!}{1!.9!}\times \frac{5!}{1!.4!}+\frac{10!}{2!.8!}}{\frac{15!}{2!.13!}} \\ &= \frac{\frac{10.9!!}{1.9!}\times \frac{5.4!!}{1.4!}+\frac{10.9.8!}{2.1.8!}}{\frac{15.14.13!}{2.1.13!}} \\ &= \frac{10\times 5+45}{105} \\ &= \frac{95}{105} \\ \frac{m}{n} &= \frac{19}{21} \end{align}$$m+n=19+21=40$
Answer: C
SEAMO 2017 Paper D No. 21
In an equilateral $\Delta ABC$, D and E are points on BC and AB respectively. Given that BD = AE and AD and CE intersect at point F, find $\angle DFC$.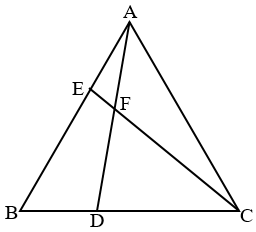
A. $30^\circ$
B. $36^\circ$
C. $42^\circ$
D. $54^\circ$
E. $60^\circ$
Solution: Show/Hide
$\angle A=\angle B=\angle C=60^\circ$AB = BC = AC
In $\Delta ABD$ and $\Delta CAE$:
AB = AC
$\angle ABD=\angle CAE$
BD = AE (given)
$\therefore \Delta ABD\cong \Delta CAE$
Now, $\angle BAD+\angle DAC=\angle BAC=60^\circ$
$\angle ACE+\angle DAC=60^\circ$;
$\angle AFC=180^\circ -60^\circ =120^\circ$
$\begin{align}\angle DFC &= 180^\circ -\angle AFC \\ &= 180^\circ -120^\circ \\ &= 60^\circ \end{align}$
Answer: E
SEAMO 2017 Paper D No. 22
The number which, when subtracted from the terms of ratio $a:b$ makes it equal to $c:d$, isA. $\frac{ab-cd}{ab+cd}$
B. $\frac{bc-ad}{c-d}$
C. $\frac{ab+cd}{c+d}$
D. $\frac{ab-cd}{b-c}$
E. None of the above
Solution: Show/Hide
$\frac{a-x}{b-x}=\frac{c}{d}$Cross multiply:
$\begin{align}(a-x)d &= c(b-x) \\ ad-xd &= cb-cx \\ cx-dx &= cb-ad \\ x(c-d) &= cb-ad \\ x &= \frac{cb-ad}{c-d} \end{align}$
Answer: B
SEAMO 2017 Paper D No. 23
$a$, $b$, $c$ are three positive real numbers. $c$ is greater than $b$ by the amount that $b$ is greater than $a$. The product of the two smaller numbers is 85 and that of the two bigger numbers is 115. Then the value of $(2012a-1006c)$ isA. 3355
B. 4433
C. 5533
D. 3344
E. 5454
Solution: Show/Hide
$a < b < c$Let $a=A-D$, $b=A$, $c=A+D$
$\begin{align}\frac{(A-D)A}{A(A+D)} &= \frac{85}{115} \\ \frac{A-D}{A+D} &= \frac{17}{23} \\ 23A-23D &= 17A+17D \\ 6A &= 40D \\ 3A &= 20D \\ A &= \frac{20D}{3} \end{align}$
$\begin{align}(A-D)A &= 85 \\ \left( \frac{20D}{3}-D \right).\frac{20D}{3} &= 85 \\ \frac{17D}{3}.\frac{20D}{3} &= 85 \\ 17.20D^2 &= 9.85 \\ 4D^2 &= 9 \\ D^2 &= \frac{9}{4} \\ D &= \frac{3}{2} \end{align}$
$\begin{align}A &= \frac{20}{3}D \\ &= \frac{20}{3}.\frac{3}{2} \\ A &= 10 \end{align}$
$\begin{align}a &= A-D \\ &= 10-\frac{3}{2} \\ a &= \frac{17}{2} \end{align}$
$\begin{align}c &= A+D \\ &= 10+\frac{3}{2} \\ c &= \frac{23}{2} \end{align}$
$\begin{align}2012a-1006c &= 1006(2a-c) \\ &= 1006\left( 2.\frac{17}{2}-\frac{23}{2} \right) \\ &= 1006.\frac{11}{2} \\ &= 5533 \end{align}$
Answer: C
SEAMO 2017 Paper D No. 24
If $x=\frac{y}{y+1}$ and $y=\frac{a-2}{2}$, then value of $x(y+2)+\frac{x}{y}+\frac{y}{x}$ when $a=2017$ isA. 2016
B. 2015
C. 2018
D. 2017
E. 2019
Solution: Show/Hide
$y=\frac{a-2}{2}$$\begin{align}x &= \frac{y}{y+1} \\ &= \frac{\frac{(a-2)}{2}}{\frac{(a-2)}{2}+1} \\ x &= \frac{a-2}{a} \end{align}$
$\frac{x}{y}=\frac{\frac{a-2}{a}}{\frac{a-2}{2}}\to \frac{x}{y}=\frac{2}{a}$
$x(y+2)+\frac{x}{y}+\frac{y}{x}$
= $\frac{a-2}{a}\left( \frac{a-2}{2}+2 \right)+\frac{2}{a}+\frac{a}{2}$
= $\frac{a-2}{a}.\frac{a+2}{2}+\frac{4+a^2}{2a}$
= $\frac{a^2-4}{2a}+\frac{4+a^2}{2a}$
= $\frac{2a^2}{a}$
= $a$
= 2017
Answer: D
SEAMO 2017 Paper D No. 25
A triangular pyramid is made of 4 equilateral triangles as faces. If each side of equilateral triangular face is 1 unit, find the height of the pyramid.A. $\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}$
B. $\sqrt{\frac{3}{2}}$
C. $\frac{2}{\sqrt{3}}$
D. $\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$
E. None of the above
Solution: Show/Hide

$b=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}a$
Height of the pyramid : $H=\sqrt{a^2-b^2}$
$\begin{align}H &= \sqrt{a^2-\left( \frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}a \right)^2} \\ &= \sqrt{a^2-\frac{1}{3}a^2} \\ &= \sqrt{\frac{2}{3}a^2} \\ H &= a\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}} \end{align}$
$a=1$
$H=a\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}=1.\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}=\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}$
Answer: A

Post a Comment for "Solution of SEAMO 2017 Paper D - Southeast Asian Mathematical Olympiads"
Pertanyaan melalui kolom komentar akan direspon secepatnya. Jika tidak direspon, berarti pertanyaan serupa telah ada.